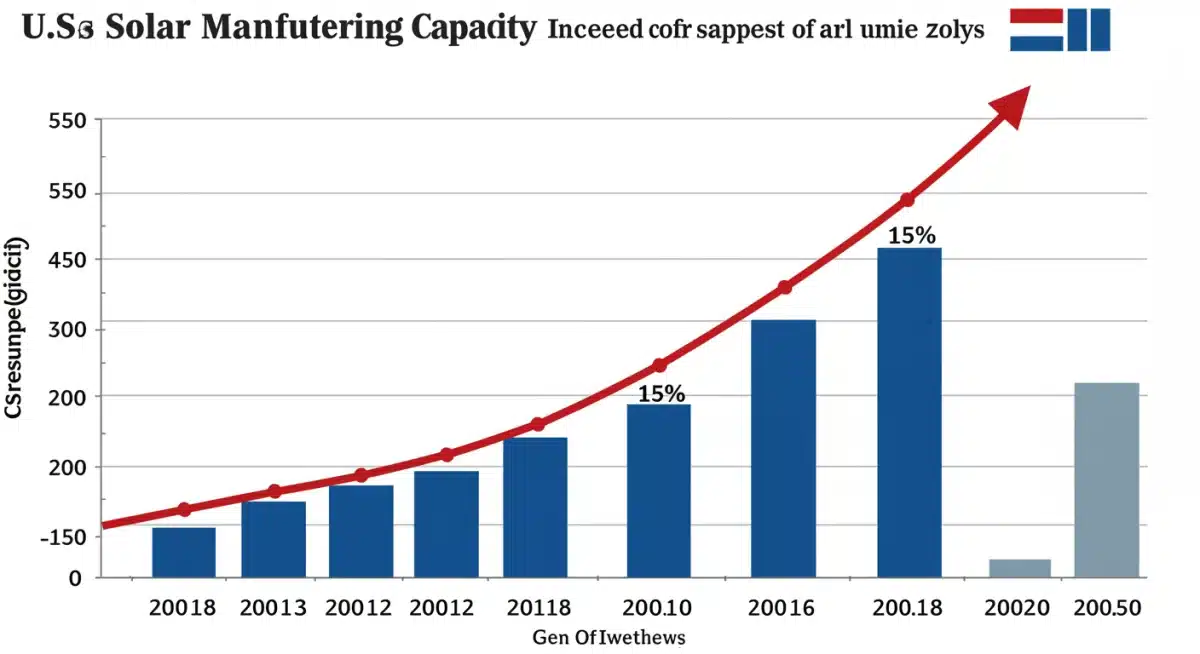
U.S. Solar Manufacturing Surges 15%, Exceeding 2025 Projections

A new report confirms a significant 15% rise in U.S. solar manufacturing capacity over the past six months, exceeding initial 2025 projections and demonstrating accelerated national progress in renewable energy production.
A groundbreaking new report has revealed a monumental U.S. solar manufacturing surge, with capacity increasing by an impressive 15% in just the last six months alone. This remarkable growth not only highlights a pivotal moment for the nation’s clean energy ambitions but also significantly surpasses the projections initially set for 2025, signaling a robust and accelerating shift towards domestic renewable energy production.
The Unprecedented Growth of U.S. Solar Manufacturing
The recent findings from a comprehensive industry report paint a vivid picture of rapid expansion within the United States’ solar manufacturing sector. This unprecedented growth is not merely an incremental step but a significant leap forward, demonstrating a clear commitment to fostering a robust domestic supply chain for solar energy components. The 15% increase in capacity within a mere six-month period is a testament to the effectiveness of recent policy initiatives and private sector investments.
This surge is particularly noteworthy as it outpaces even the most optimistic forecasts, indicating a stronger-than-anticipated rebound and acceleration in the industry. The implications are far-reaching, affecting everything from energy independence to job creation and environmental sustainability. Understanding the drivers behind this rapid expansion is crucial for appreciating its potential long-term impact on the national energy landscape.
Key Drivers Behind the Surge
Several factors have converged to create this environment of accelerated growth. Government incentives, technological advancements, and increasing consumer demand for sustainable energy solutions have all played critical roles. These elements have collectively spurred both new investments and the expansion of existing facilities across the country.
- Policy Support: Federal and state policies, such as tax credits and manufacturing incentives, have significantly de-risked investments in domestic solar production, making it more attractive for companies to establish or expand operations within the U.S.
- Technological Innovation: Continuous improvements in solar panel efficiency and manufacturing processes have made U.S.-produced solar components more competitive and desirable.
- Supply Chain Resilience: A growing desire to reduce reliance on foreign supply chains, especially in critical sectors, has pushed for greater domestic manufacturing capabilities.
The combined effect of these drivers has created a powerful momentum, propelling the U.S. solar manufacturing sector into a new era of growth and self-sufficiency. This foundation is critical for ensuring the nation’s energy security and its leadership in the global clean energy transition.
Exceeding 2025 Projections: A New Benchmark
The fact that U.S. solar manufacturing capacity has exceeded 2025 projections almost two years ahead of schedule is a monumental achievement. This milestone not only validates the strategic investments made but also sets a new benchmark for future growth trajectories. The initial projections, while ambitious at the time, clearly underestimated the pace at which the industry could mobilize and expand under favorable conditions.
This early overachievement signals a robust and dynamic market, eager to embrace renewable energy solutions. It also reflects a heightened sense of urgency and commitment from both public and private entities to accelerate the clean energy transition. The implications for meeting national climate goals and fostering economic resilience are profound, suggesting that the U.S. is well on its way to becoming a global leader in solar technology production.
The Role of the Inflation Reduction Act
A significant catalyst for this accelerated growth has been the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). Enacted to stimulate domestic manufacturing and clean energy deployment, the IRA has provided substantial incentives that have directly impacted the solar sector. These incentives include manufacturing tax credits, which have made it economically viable for companies to produce solar components within the United States rather than importing them.
The foresight embedded in the IRA’s provisions has clearly paid off, creating a tangible impact on manufacturing output and capacity. It has fostered an environment where companies are not only willing but eager to invest in American-made solar technology, creating thousands of new jobs and revitalizing manufacturing communities. This legislative framework has proven to be a powerful engine for industrial growth and innovation.
Economic Impact and Job Creation
The surge in U.S. solar manufacturing capacity brings with it a wave of positive economic impacts, most notably in job creation. The establishment and expansion of manufacturing facilities require a skilled workforce, leading to the creation of thousands of new jobs across various sectors, from engineering and production to logistics and management. These are often well-paying jobs that contribute significantly to local economies.
Beyond direct manufacturing roles, the ripple effect extends to ancillary industries that support the solar supply chain, including raw material suppliers, equipment manufacturers, and service providers. This creates a broader economic ecosystem that benefits from the growth of the solar sector. The investment in domestic manufacturing also reduces reliance on foreign imports, keeping more capital within the national economy and strengthening economic resilience.
Regional Economic Benefits
The economic benefits are often concentrated in specific regions where new factories are being built or expanded. These areas experience a boost in local employment, increased tax revenues, and greater economic stability. Communities that were once dependent on traditional industries are now finding new opportunities in the clean energy sector, leading to economic diversification and revitalization.
- Increased Local Employment: New solar manufacturing plants directly create jobs for engineers, technicians, assembly line workers, and administrative staff.
- Supply Chain Development: Growth in solar manufacturing stimulates demand for upstream industries, fostering local businesses that supply materials and services.
- Tax Revenue Growth: Increased industrial activity and employment lead to higher local and state tax revenues, which can be reinvested in community services and infrastructure.
These regional impacts are crucial for ensuring that the benefits of the clean energy transition are distributed equitably across the nation, supporting a just transition for all communities.
Technological Advancements and Innovation
The rapid expansion of U.S. solar manufacturing is not just about scaling up production; it is also intrinsically linked to significant technological advancements and innovation. As domestic manufacturers ramp up their capabilities, there is a strong emphasis on developing more efficient, durable, and cost-effective solar technologies. This drive for innovation is essential for maintaining a competitive edge in the global market.
Research and development efforts are focused on improving every aspect of solar panel production, from the quality of silicon wafers to the design of photovoltaic cells and the integration of smart technologies. These advancements not only enhance the performance of solar panels but also contribute to lowering the overall cost of solar energy, making it an even more attractive option for consumers and businesses alike.
Future of Solar Technology
The future of solar technology in the U.S. is bright, with ongoing research exploring next-generation materials like perovskites, bifacial panels, and advanced energy storage solutions. These innovations promise to further boost efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and expand the applicability of solar power to a wider range of settings. Investing in domestic manufacturing also means investing in the intellectual capital and infrastructure needed to lead these technological frontiers.
This commitment to innovation ensures that the U.S. remains at the forefront of solar technology, driving global progress and setting new standards for efficiency and sustainability. The synergy between manufacturing growth and technological advancement creates a virtuous cycle, where each feeds into the other, accelerating the pace of progress.
Environmental Benefits and Energy Independence
The heightened solar manufacturing capacity in the U.S. carries substantial environmental benefits, primarily through the reduction of carbon emissions. By producing more solar panels domestically, the nation can accelerate its transition away from fossil fuels, thereby mitigating climate change and improving air quality. This shift towards renewable energy is a critical component of national and global sustainability efforts.
Furthermore, increased domestic production contributes significantly to energy independence. Reducing reliance on imported energy sources and components strengthens national security and economic stability. A robust domestic solar supply chain means less vulnerability to geopolitical disruptions and volatile international markets, providing a more reliable and sustainable energy future for the United States.
Path Towards a Sustainable Future
The environmental advantages extend beyond just energy generation. Domestic manufacturing can also adhere to stricter environmental regulations and ethical labor practices compared to some overseas production, ensuring that the entire lifecycle of solar products is more sustainable. This holistic approach to sustainability reinforces the long-term benefits of a localized solar industry.
- Reduced Carbon Footprint: Increased solar deployment directly displaces fossil fuel electricity generation, leading to significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions.
- Cleaner Air and Water: Less reliance on conventional power plants results in fewer pollutants, improving public health and ecosystem quality.
- Enhanced Energy Security: A domestic supply chain for solar technology reduces dependence on foreign energy sources and enhances national resilience.
This progressive movement towards greater energy independence and environmental stewardship positions the U.S. as a leader in the global fight against climate change, setting an example for other nations to follow.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While the recent surge in U.S. solar manufacturing capacity is highly encouraging, the sector still faces certain challenges that need to be addressed to sustain this momentum. These include ensuring a consistent supply of raw materials, addressing labor shortages, and competing with established international markets. Overcoming these hurdles will be crucial for the industry’s continued growth and long-term success.
Despite these challenges, the future outlook for U.S. solar manufacturing remains overwhelmingly positive. The strong foundation laid by recent policy support, coupled with ongoing technological innovation and increasing demand for clean energy, suggests a trajectory of sustained growth. The goal is not just to maintain current capacity but to further expand it, making the U.S. a powerhouse in global solar production.
Strategies for Sustained Growth
To ensure continued growth, stakeholders will need to focus on several strategic areas. These include investing in workforce development programs to train the next generation of solar manufacturing professionals, fostering greater collaboration between industry and academia, and exploring new avenues for technological advancements. Policies that support a stable and predictable regulatory environment will also be vital.
- Workforce Development: Implementing training programs and educational initiatives to build a skilled labor force for the expanding solar manufacturing sector.
- Raw Material Sourcing: Developing robust domestic supply chains for critical raw materials to minimize reliance on foreign sources and ensure production stability.
- R&D Investment: Continued investment in research and development to drive technological innovation and maintain a competitive edge in solar efficiency and cost.
By proactively addressing these areas, the U.S. can solidify its position as a global leader in solar manufacturing, driving economic prosperity and environmental sustainability for decades to come.
| Key Point | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 15% Capacity Increase | U.S. solar manufacturing capacity grew by 15% in the last six months, a significant and rapid expansion. |
| Exceeded 2025 Projections | This growth surpassed initial forecasts for 2025, highlighting accelerated progress in domestic solar production. |
| Economic & Job Growth | The surge is creating thousands of new jobs and boosting local economies across the nation. |
| Policy Impact | Federal policies, particularly the Inflation Reduction Act, are key drivers behind this rapid expansion. |
Frequently Asked Questions About U.S. Solar Manufacturing
This 15% increase signifies a robust and accelerated growth in the domestic production of solar energy components. It indicates a strong commitment to strengthening the U.S. clean energy supply chain, reducing reliance on foreign imports, and achieving energy independence faster than anticipated.
The early overachievement is largely attributed to impactful government policies, particularly the Inflation Reduction Act, which provides significant manufacturing tax credits and incentives. These policies, combined with private sector investments and technological advancements, have spurred rapid expansion and efficiency gains.
The surge is creating thousands of new, well-paying jobs across various sectors, from engineering to production. It also boosts local economies through increased tax revenues, stimulates growth in related industries, and strengthens overall economic resilience by keeping capital within the national economy.
Technological advancements are crucial. Innovations in solar panel efficiency, durability, and manufacturing processes make U.S.-produced components more competitive. Ongoing R&D in areas like perovskites and advanced storage solutions further drives down costs and expands the applicability of solar power, sustaining future growth.
Despite rapid growth, challenges remain, including ensuring a consistent supply of raw materials, addressing potential labor shortages, and maintaining competitiveness against global markets. Strategic investments in workforce development and continued policy support are essential to overcome these hurdles and sustain long-term growth.
Conclusion
The recent report detailing a 15% increase in U.S. solar manufacturing capacity within the last six months, significantly surpassing 2025 projections, marks a pivotal moment for the nation’s clean energy future. This remarkable achievement underscores the effectiveness of strategic policy interventions, robust private sector investment, and a growing commitment to energy independence. The ripple effects of this surge are profound, promising not only substantial economic growth and job creation but also accelerating the transition to a sustainable, low-carbon economy. While challenges persist, the current momentum suggests a bright and self-sufficient future for solar energy in the United States, cementing its role as a global leader in renewable technology and production.





